COMMUNICATION SKILLS – SOFT SKILLS CLUSTER
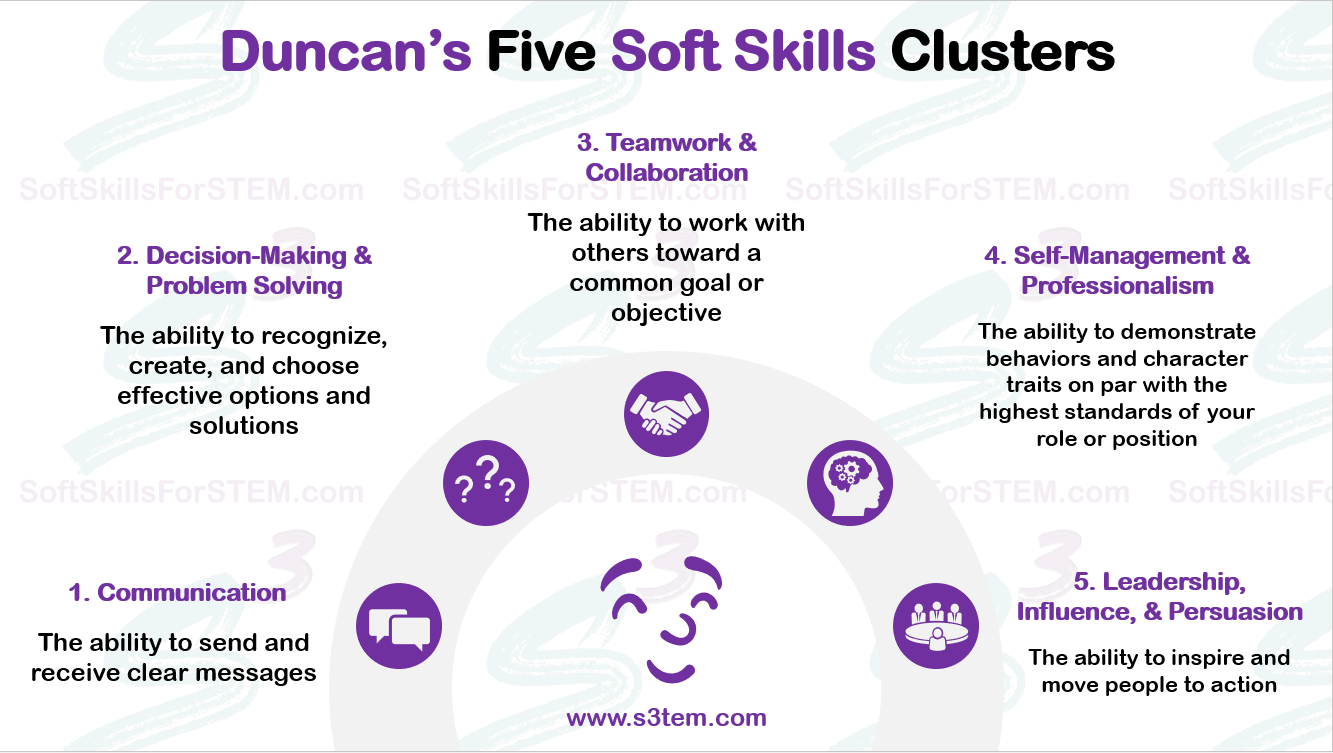
List of Soft Skills Clusters (Beta – That means I’m still working on this. Thanks for you patience.)
Main Page of Soft Skills Clusters
(Sources listed at the bottom of main page.)
Communication Skills
Decision Making & Problem Solving Skills
Teamwork & Collaboration Skills
Self-Management & Professionalism Skills
Leadership, Influence & Persuasion Skills
Key Behavioral indicators
This is how you demonstrate that you have strong communication skills.
Verbal (Oral) Communication
- Watch and listen attentively for the reactions and feelings being expressed by others.
- Use words and phrases accurately.
- Speak using proper grammar.
- Present thoughts and ideas in a clear, concise and compelling, well-organized manner.
- Choose the most effective method of verbal communication (video conferencing, face-to-face meeting, phone conversation, presentation, etc.)
Verbal (Written) Communication
- Write using proper grammar.
- Write in a clear, concise, and compelling manner.
- Develop a logical structure and present ideas in a logical sequence.
- Clearly identify the subject and state the purpose of the communication.
- Provide a relevant conclusion or recommendation.
- Make effective use of prepared visual materials (slides, videos, & handouts).
- Choose the most effective method of communication (email, letter, social media, report, etc.)
Nonverbal Communication
- Exhibit effective body language
- Speak at an appropriate speed, volume, tone, and pitch.
- Maintain good eye contact with all listeners.
- Use appropriate non-verbal communications (gestures, posture, facial expression and mannerisms).
individual skills
These are the skills you develop to produce the desired behavioral indicators.
Active Listening: Being completely focused and engaged in what the sender is saying.
Tip: Here’s the key to active listening in 3 words: Show genuine interest. (paraphrasing Dale Carnegie, author of How To Win Friends and Influence People)
“Most people aren’t listening to what the other person is saying, they are just waiting for their turn to talk.” —George Carlin, comedian
Duncan Nugget® #358:
Distraction and interruption are the arch enemies of active listening. You can conquer them by showing genuine interest in the other person.
Sometimes the listener doesn’t even realize that he has been distracted until the person communicating solicits a response. (“Are you even listening to me?” “Yeah…uh…I heard everything you said…”)
The listener has to make a conscious effort to hear the words AND understand the message. Evidence of active listening and genuine interest can be found in aspects of verbal and nonverbal feedback.
Verbal Feedback
- Asking relevant questions and seeking clarification. (This is not the same as asking for repetition due to lack of attention.)
- Summarizing and paraphrasing (This shows that you understand and remember.)
- Non-interruptive comments (yes, uh huh, Mmm hmm, really?, wow, amen, oh no she didn’t!)
Nonverbal Feedback
- Body language such as eye contact, smiling, frowning, head nodding,
- Mirroring (adopting body language, expressions, and emotions similar to the sender.)
Communication: The exchange of information between people by means of speaking, writing, or using a common system of symbols, signs, or behavior. Communication requires a sender, a message, and an intended recipient. The communication process is complete once the recipient has understood the sender.
Tip: Communication is a primary soft skill. It’s not even possible to master most soft skills without effective communication skills.
Duncan Nugget® #359:
When you communicate, you shape a person’s perception of who you are.
WHAT EMPLOYERS, COLLEGES, & GRAD SCHOOLS WANT
Verbal (Oral) Communication: ideal candidates, applicants, and employees can articulate thoughts and ideas clearly and effectively to another individual or group (presentations, speeches, conference calls, etc.)
Nonverbal Communication: the process of communication through sending and receiving wordless cues between people.
A well-known saying about nonverbal communication: “It’s not what you say, it’s how you say it?”
Forms of nonverbal communication include:
— Appearance/Environment (Visual)
— Body language (kinesics)
— Voice (inflection; paralanguage;)
— Touch (haptics)
— Distance (proxemics)
A few behaviors that demonstrate effective verbal and nonverbal communication in the workplace or school:
- Listen attentively
- Ask good questions
- Give the appropriate amount of eye contact.
- Communicate pleasantly and professionally with co-workers, clients, customers, classmates, teachers, professors, etc.
Written Communication: Ideal candidates, applicants, and employees can write memos, letters, emails and complex technical reports clearly and effectively as well as use social media appropriately.
A well-known quote about writing: “The pen is mightier than the sword.” —Edward Bulwer-Lytton
According to a report from The College Board the most in-demand aspects of writing are:
— accuracy
— clarity
— spelling
— punctuation
— grammar
— conciseness
Negotiation:
Public Speaking: A form of verbal communication. Check out public speaking tips.
Rapport:
Storytelling: How to Tell Your Story In Professional Settings
List of Soft Skills Clusters
Main Page of Soft Skills Clusters
(Sources listed at the bottom of main page.)
Communication Skills
Decision Making & Problem Solving Skills
Teamwork & Collaboration Skills
Self-Management & Professionalism Skills
Leadership, Influence & Persuasion Skills